Google Maps Extractors: Finding New Leads Through Data Collection
ArticleA Google Maps Extractor is a tool designed to automate the process of retrieving data from Google Maps. It enables users to collect vital information such as business names, addresses, phone numbers, reviews, ratings, and more.
 Google Maps is an incredibly rich source of business information, providing everything from company names and contact details to customer reviews and geographical data. However, manually gathering this information can be tedious. That's where a Google Maps Extractor comes into play, enabling you to pull this data effortlessly for a variety of applications such as lead generation, market analysis, and competitor research.
Google Maps is an incredibly rich source of business information, providing everything from company names and contact details to customer reviews and geographical data. However, manually gathering this information can be tedious. That's where a Google Maps Extractor comes into play, enabling you to pull this data effortlessly for a variety of applications such as lead generation, market analysis, and competitor research.
What is a Google Maps Extractor?
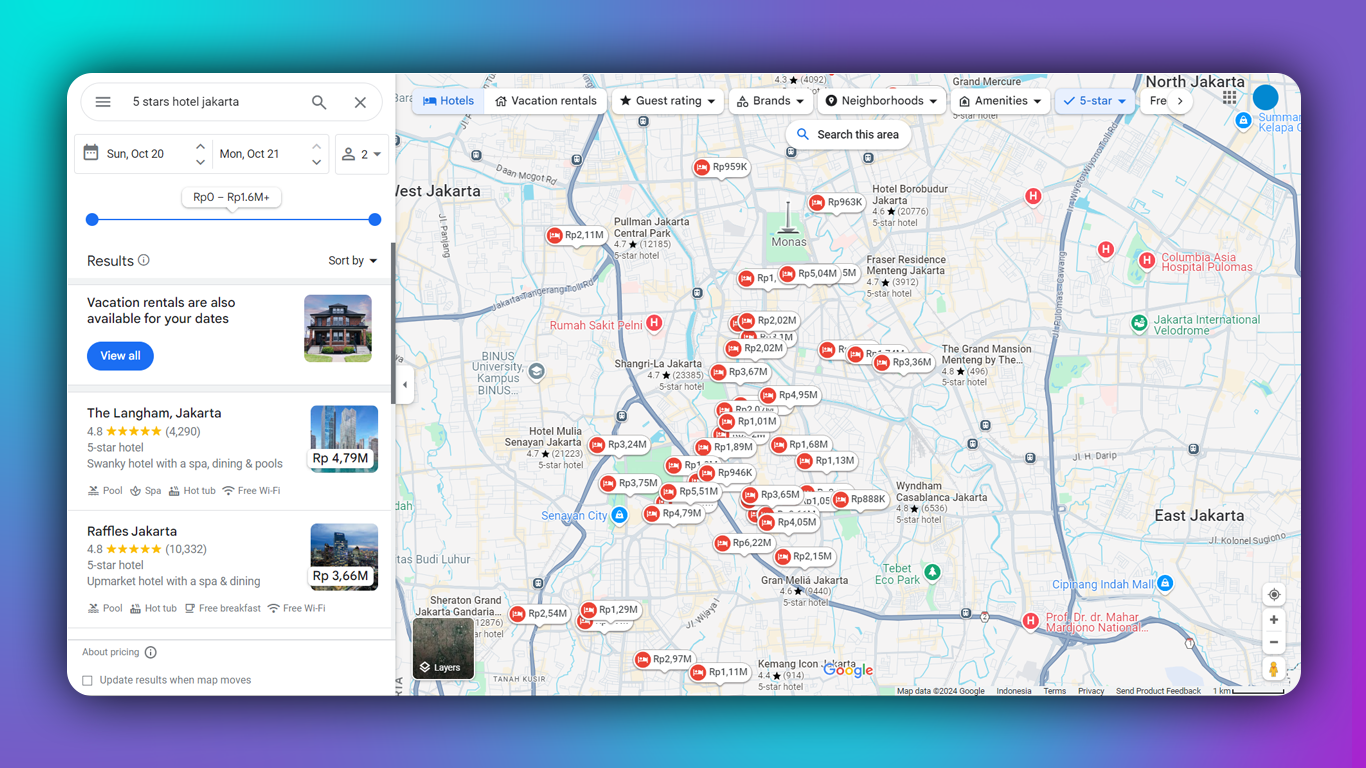
A Google Maps Extractor is a tool designed to automate the process of retrieving data from Google Maps. It enables users to collect vital information such as business names, addresses, phone numbers, reviews, ratings, and more. Whether you are building a list of potential clients or conducting market research, this tool saves hours of manual work by scraping data based on your chosen keywords.
For instance, you might use a Google Maps Data Extractor to find all the hotels within a specific area, pull their contact details, and analyze customer reviews. Similarly, it's widely used for building business lead databases, helping marketing teams and sales professionals reach out to potential clients more efficiently.
Why Use a Google Maps Extractor?
- Lead Generation: Build comprehensive lists of businesses in your target market.
- Competitor Analysis: Gather competitor data and analyze customer feedback.
- Customer Reviews: Extract and analyze reviews to understand market trends.
- Localized Data: Find businesses in a particular geographical region for marketing or outreach.
How to Use a Google Maps Extractor with Python
Below is an example of how you can use Python along with the Selenium library to extract data from Google Maps.
Prerequisites
- Install required libraries:
pip install selenium
- Download a WebDriver (e.g., ChromeDriver) and add it to your system’s PATH.
Example Code
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service
from webdriver_manager.chrome import ChromeDriverManager
import time
#Setup ChromeDriver
options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
options.add_argument('--headless')
driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=Service(ChromeDriverManager().install()), options=options)
#Function to search businesses on Google Maps
def search_business_on_maps(query, location):
search_url = f'https://www.google.com/maps/search/{query}+in+{location}/'
driver.get(search_url)
time.sleep(5) # Allow page to load
business_data = []
# Scraping business information
businesses = driver.find_elements(By.CLASS_NAME, 'section-result-text-content')
for business in businesses:
name = business.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, 'section-result-title').text
address = business.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, 'section-result-location').text
try:
phone = business.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, 'section-result-phone-number').text
except:
phone = 'N/A'
business_data.append({
'name': name,
'address': address,
'phone': phone
})
return business_data
#Example usage
query = "restaurants"
location = "New York"
data = search_business_on_maps(query, location)
for business in data:
print(business)
#Cleanup
driver.quit()
This Python script uses Selenium to automate the Google Maps search for businesses in a specific location. It scrapes business names, addresses, and phone numbers and stores them in a structured format.
Integrating Real-Time Data Extraction with a Google Scraper API
For more scalable solutions, a Google Scraper API can automate the process without the need for manual setup or browser automation. Here’s an example of how to use an API to extract Google Maps data.
Sample API Request with Python
Below is an example of how you can interact with the Google Scraper API using Python to retrieve real-time business data from Google Maps.
- Install the required library for making HTTP requests:
pip install requests
- Example code to query the API:
import requests
#Set up your API key and endpoint
API_KEY = 'your_mrscraper_api_key'
endpoint = 'https://api.mrscraper.com/maps'
#Define query parameters
params = {
'api_key': API_KEY,
'query': 'restaurants',
'location': 'New York, NY',
'radius': 5000, # Radius in meters
'type': 'restaurant'
}
#Make the API request
response = requests.get(endpoint, params=params)
#Check for successful response
if response.status_code == 200:
data = response.json()
for business in data['results']:
print(f"Name: {business['name']}")
print(f"Address: {business['formatted_address']}")
print(f"Phone: {business.get('formatted_phone_number', 'N/A')}")
print()
else:
print(f"Error: {response.status_code}")
This Python script makes a GET request to the Google Scraper API, fetching business listings for restaurants within a specified radius of New York City. The data is returned in a structured JSON format, which you can easily parse and use in your application.
Handling Rate Limits and Anti-Scraping Measures
Google Maps employs several anti-scraping mechanisms such as rate limits, IP blocking, and CAPTCHAs. To build a robust extractor, these challenges must be addressed:
- Proxy Rotation: Use a pool of rotating proxies to distribute requests across different IPs and avoid rate-limiting.
- CAPTCHA Solvers: Integrate third-party CAPTCHA solving services to handle Google’s reCAPTCHA challenges.
- Headless Browsing: Employ headless browsers like Puppeteer or Selenium to mimic human behavior and dynamically render content.
Scraping Google Maps at scale requires balancing request frequency and optimizing headers, cookies, and referrers to avoid detection. Proper error handling mechanisms (e.g., backoff strategies) ensure continuous scraping without interruptions.
Free and Paid Options
There are both free and paid tools available for Google Maps Lead Extraction. Free versions may offer basic functionality and are a good starting point for small-scale projects or personal use. However, for businesses needing consistent, large-scale data, a professional solution—often with an API integration—is more suited for the job. These paid services generally come with additional features like proxy handling, faster scraping speeds, and access to a broader set of data points.
Conclusion
Automating data collection from Google Maps is invaluable for businesses that rely on up-to-date, accurate information for lead generation and market research. With MrScraper, you can effortlessly extract the data you need and unlock insights to drive your business forward. Whether you’re using the Google Maps Extractor or integrating the Google Scraper API, MrScraper makes the process of data extraction more efficient, scalable, and reliable. To learn more about automating your data collection, check out our guide to "No-Code Google SERP Scraping", where we explore more powerful scraping techniques.
Find more insights here

Scrape Bing Search: A Practical Technical Guide
Bing scraping blocked? Discover how to bypass rate limits and bot detection to extract URLs, titles,...

FilterBypass: Unblocking Restricted Sites in a Simple Way
FilterBypass is a free web proxy that acts as an intermediary between your browser and the target si...

YouTube.com Unblocked: Accessing YouTube When It’s Restricted
Learn how to access YouTube unblocked on school, work, or regional networks. Explore VPNs, proxies,...
